티스토리 뷰
Join
앞 포스팅에서 Thread.sleep() 메서드를 통해 TIMED_WAITING 상태를 알아보았다. 이번에는 join() 메서드를 통해 WAITING(대기 상태)가 무엇이고 왜 필요한지 알아보자.
Waiting (대기 상태)
- 스레드가 다른 스레드의 특정 작업이 완료되기를 무기한 기다리는 상태이다.
public class JoinMainV0 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
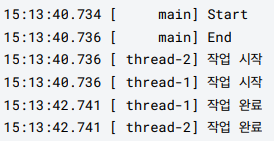
log("Start");
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Job(), "thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Job(), "thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
log("End");
}
static class Job implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
log("작업 시작");
sleep(2000);
log("작업 완료");
}
}
}
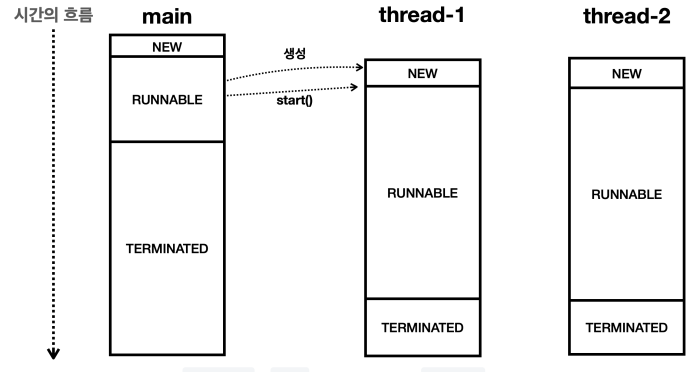
main 스레드는 thread-1, thread-2을 실행하고 바로 자신의 다음 코드를 실행한다. 여기서 핵심은 main 스레드가 thread-1,thread-2 가 끝날때까지 기다리지 않는 점이다. main 스레드는 단지 start()를 호출해서 다른 스레드를 실행만 하고 바로 자신의 다음 코드를 실행한다.
그런데 만약 thread-1 , thread-2 가 종료된 다음에 main 스레드를 가장 마지막에 종료하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
예를 들어서 main 스레드가 thread-1,thread-2에 각각 어떤 작업을 지시하고, 그 결과를 받아서 처리하고 싶다면?
Join - 필요한 상황
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
1부터 100까지 더하는 간단한 코드를 작성했다.
CPU 코어를 더 효율적으로 사용하려면 여러 스레드로 나누어 계산하면된다.
1번 스레드는 1~50 까지 더하기 = 1275
2번 스레드는 51~100 까지 더하기 = 3775
public class JoinMainV1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
log("Start");
SumTask task1 = new SumTask(1, 50);
SumTask task2 = new SumTask(51, 100);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task1, "thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task2, "thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
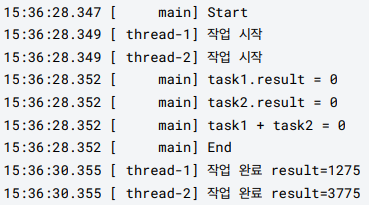
log("task1.result = " + task1.result);
log("task2.result = " + task2.result);
int sumAll = task1.result + task2.result;
log("task1 + task2 = " + sumAll);
log("End");
}
static class SumTask implements Runnable {
int startValue;
int endValue;
int result = 0;
public SumTask(int startValue, int endValue) {
this.startValue = startValue;
this.endValue = endValue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log("작업 시작");
sleep(2000);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = startValue; i <= endValue; i++) {
sum += i;
}
result = sum;
log("작업 완료 result=" + result);
}
}
}
우리 생각대로라면 sumAll은 5050을 출력해야한다.
결과는 어떨까?
결과는 0이 나온다.
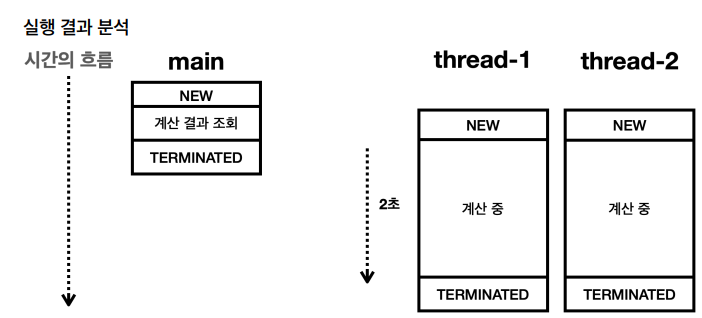
main 스레드는 thread-1 thread-2에 작업을 지시하고, thread-1 thread-2가 계산을 완료하기도 전에 먼저 계산 결과를 조회했다.
Join 사용
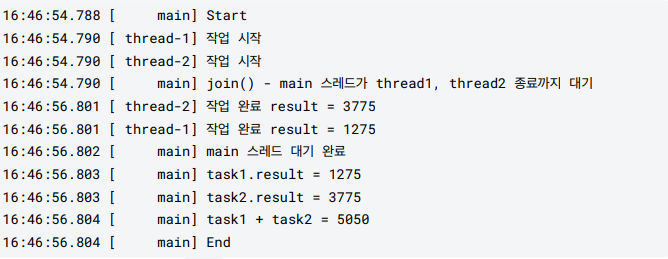
public class JoinMainV3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
log("Start");
SumTask task1 = new SumTask(1, 50);
SumTask task2 = new SumTask(51, 100);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task1, "thread-1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task2, "thread-2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
// 스레드가 종료될 때 까지 대기
log("join() - main 스레드가 thread1, thread2 종료까지 대기");
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
log("main 스레드 대기 완료");
log("task1.result = " + task1.result);
log("task2.result = " + task2.result);
int sumAll = task1.result + task2.result;
log("task1 + task2 = " + sumAll);
log("End");
}
static class SumTask implements Runnable {
int startValue;
int endValue;
int result = 0;
public SumTask(int startValue, int endValue) {
this.startValue = startValue;
this.endValue = endValue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log("작업 시작");
sleep(2000);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = startValue; i <= endValue; i++) {
sum += i;
}
result = sum;
log("작업 완료 result = " + result);
}
}
}
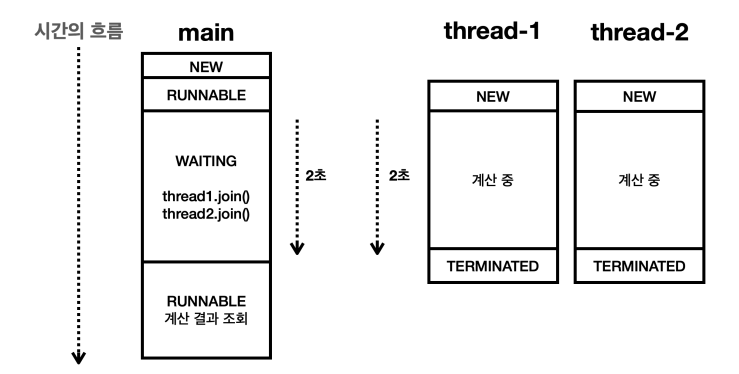
main 스레드에서 다음 코드를 실행하게 되면 main 스레드는 thread-1 thread-2 가 종료될 때 까지 기다린다.
이때 main 스레드는 WAITING 상태가 된다.
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
예를 들어 thread-1이 아직 종료되지 않았다면 main 스레드는 thread1.join() 코드 안에서 더는 진행하지 않고 멈추어 기다린다. 이후에 thread-1 이 종료되면 main 스레드는 RUNNABLE 상태가 되고 다음 코드로 이동한다.
이렇듯 특정 스레드가 완료될 떄가지 기다려야 하는 상황이라면 join()을 사용하면 된다.
하지만 무기한 기다려야한다는 단점이 존재하지만 해결방법이 존재한다.
thread1.join(1000);
위 코드 처럼 일정 시간동안만 대기 시간을 설정할 수 있다.
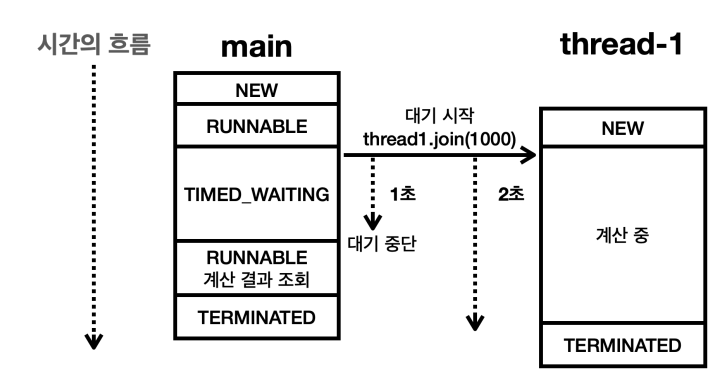
다른 스레드가 끝날 때 까지 무한정 기다려야 한다면 join() 을 사용하고, 다른 스레드의 작업을 무한정 기다릴 수 없 다면 join(ms) 를 사용하면 된다. 물론 기다리다 중간에 나오는 상황인데, 결과가 없다면 추가적인 오류 처리가 필요 할 수 있다.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java - 동기화 (Synchronzied) (0) | 2024.09.03 |
|---|---|
| Java - 메모리 가시성 (0) | 2024.08.28 |
| Java - Thread 제어와 생명 주기 (0) | 2024.08.08 |
| Java - Thread 1 (0) | 2024.07.30 |
| Java - 데이터 정렬 2 (Comparable,Comparator) (0) | 2024.06.18 |
